About VXLAN From Wikipedia: Virtual eXtensible LAN (VXLAN) is a network virtualization technology that uses a VLAN-like encapsulation technique to encapsulate OSI layer 2 Ethernet frames within layer 4 UDP datagrams, using 4789 as the default IANA-assigned destination UDP port number, although many implementations that predate the IANA assignment use port 8472. VXLAN attempts to […]
Category: Networking
Desired Port and Network Infra MAC on AOS-CX REST API
What does this mean in the HPE Networking AOS-CX REST API response when getting the MAC address tables from a switch: GET /rest/v10.08/system/vlans/*/macs/*,*… ‘dynamic,11:22:33:44:55:66’: { ‘aged_on_subsystems’: {}, ‘attributes’: {‘local_move_disable’: False}, ‘denied’: False, ‘derived_entry_src’: ‘none’, ‘desired_port’: { ‘1/1/49’: ‘/rest/v10.08/system/interfaces/1%2F1%2F49’ }, ‘from’: ‘dynamic’, ‘inactivity_timeout’: 300, ‘mac_addr’: ’11:22:33:44:55:66′, ‘network_infra_mac’: False, ‘never_ageout’: False, ‘port’: None, ‘selected’: True },… Why […]
Home Assistant Was Unable to Add IKEA Matter Devices
I, for one, was quite excited when IKEA announced new Matter-based affordable smart home devices in 2025. I finally got to buy some of them and I was going to add them in my existing Home Assistant system. Specifically, for this test, I bought: They are talking with each other using Matter over Thread, the […]
F5 iControl REST API in Python
In F5 BIG-IP devices there is iControl REST API for interfacing with the devices programmatically. In this post I’ll briefly describe the basics of using the API in Python. I’ll be using BIG-IP version 17.1 here with a separately created non-administrator user account. For starters I’ll use a Python virtual environment to contain the separately-installed […]
Amazon SQS Long Polling
I’ve recently used various kinds of message queues when building various apps that have needs to communicate with other parts of the app. For remote use, when the messaging parties are not on the same host, I’ve mostly used Amazon SQS, the Simple Queue Service. When using the SQS ReceiveMessage API call you can select […]
Docker Networking with Zabbix Proxies
Let’s do some Docker networking with Zabbix proxies. The presented Docker configurations apply to other similar client-server applications as well, so you may find this useful even if you don’t use Zabbix. On this longish page: Preparations I’m running the Docker service on Debian Linux 12 on a virtual machine, with no special configurations. These […]
VRRP with Keepalived
VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) is commonly used for providing first-hop IPv4 or IPv6 router (“default gateway”) redundancy for network-attached devices. Some network appliances like wireless LAN controllers use it to provide a virtual IP that can always be used for reaching the active member in the device cluster. VRRP can also be used on […]
MAC Address Move in VM Live Migration
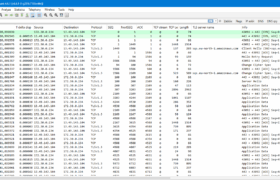
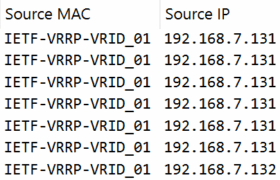
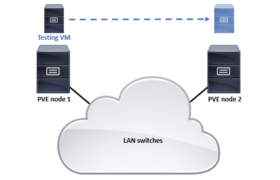
The switches in Ethernet networks learn all connected hosts’ link-layer addresses (layer 2 or MAC (Media Access Control) addresses) dynamically when the hosts communicate in the network and the switches see the traffic. Based on that information the switches are then able to forward frames optimally without flooding. When you disconnect a physical host from […]
Endianness
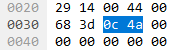
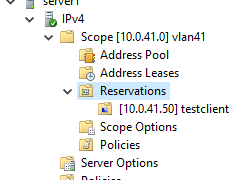
DHCP Reservations – Active or Inactive?
In DHCP servers you can configure IP address reservations, meaning that you statically configure the IP addresses that you want the specific DHCP clients to get. This is sometimes desirable when you know your devices and want to ensure that their DHCP-assigned IP addresses won’t change, because of, you know, reasons. (Printers may or may […]