When installing a Debian Linux virtual machine on a Proxmox Virtual Environment (PVE) host, the Debian installer automatically installs the VirtIO paravirtualization drivers and the QEMU guest agent so that no extra configurations are needed for full cooperation with the virtualization host.
In Windows Server 2025 those drivers and utilities are not included. It means that even the OS install is not possible without additional drivers when using the PVE-recommended Virtio SCSI disk controller.
https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Windows_VirtIO_Drivers has the instructions for getting the VirtIO driver ISO and installing the additional drivers on Windows.
Here is how you install the VirtIO SCSI driver during the OS installation (as of PVE 8.4 and VirtIO ISO 0.1.271):
- Get the VirtIO ISO from https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/archive-virtio/?C=M;O=D and save it to your storage
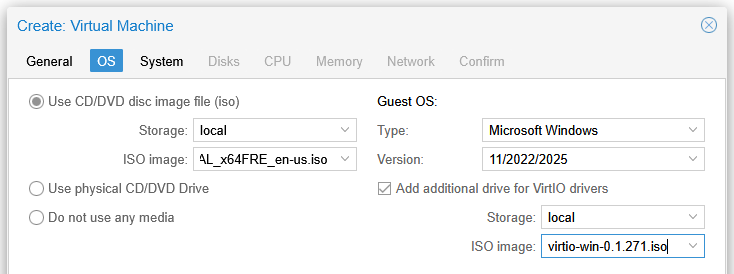
- When creating the VM, select Add additional drive for VirtIO drivers and select the ISO:
- After creating the VM and starting the Windows installer, it eventually asks you to select the location to install Windows Server:
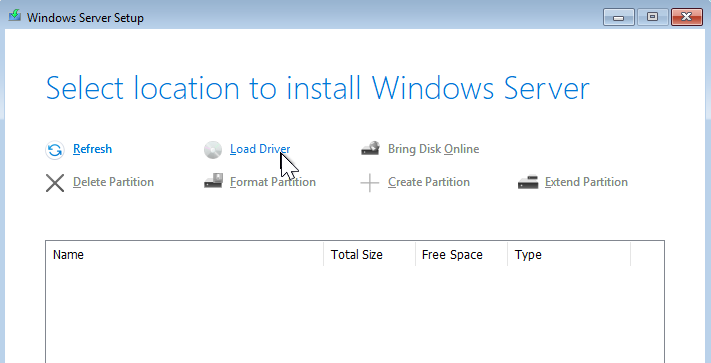
- No disks are listed, so click Load Driver and browse to
D:\vioscsi\2k25\amd64 - In the resulting list, select Red Hat VirtIO SCSI pass-through controller and click Install
- The virtual disk is now visible in the installer as “Disk 0 Unallocated Space” and you can continue partitioning it or just installing from there on.
After completing the Windows installation you can install other additional drivers and the QEMU guest agent automatically by running D:\virtio-win-guest-tools.exe.
The drivers can also be installed manually in Device Manager, by using the Update driver option for the following devices:
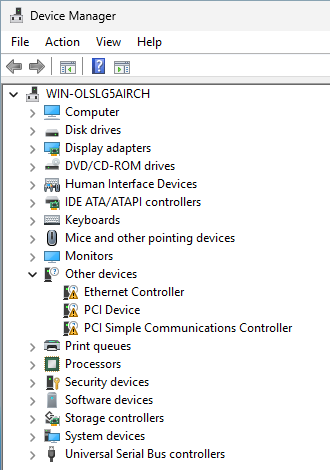
- PCI Simple Communications Controller: browse to
D:\vioserial\2k25\amd64 - PCI Device: browse to
D:\Balloon\2k25\amd64 - Ethernet Controller: browse to
D:\NetKVM\2k25\amd64 - After enabling View – Show hidden devices, there is one more unknown device, browse to
D:\qemufwcfg\2k25\amd64to update the driver for it
The QEMU guest agent can be installed manually from D:\guest-agent.